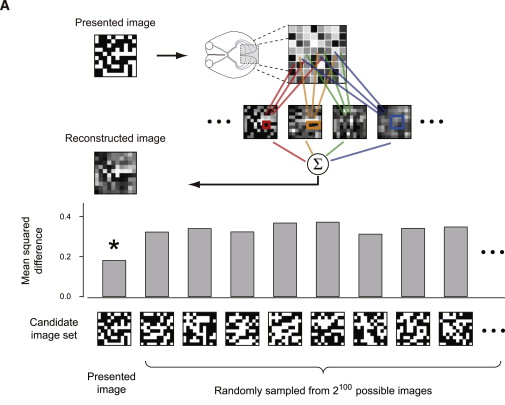
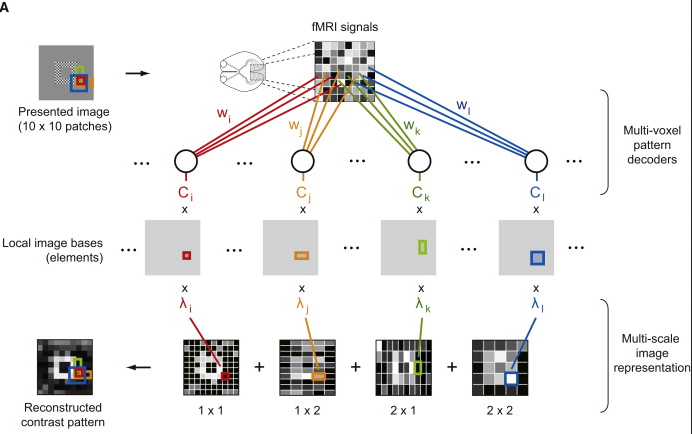
#Importing required libraries and dataset
import numpy as np
from nilearn.input_data import MultiNiftiMasker
from sklearn.linear_model import OrthogonalMatchingPursuit as OMP
from sklearn.feature_selection import f_classif, SelectKBest
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.metrics import (accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score)
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from nilearn.plotting import show
from nilearn import datasets
#Fetching the Dataset
miyawaki_dataset = datasets.fetch_miyawaki2008()
X_random = miyawaki_dataset.func[12:]
X_figure = miyawaki_dataset.func[:12]
y_random = miyawaki_dataset.label[12:]
y_figure = miyawaki_dataset.label[:12]
y_shape = (10, 10)
#Load and mask fMRI data
masker = MultiNiftiMasker(mask_img=miyawaki_dataset.mask, detrend=True, standardize=False)
masker.fit()
X_train = masker.transform(X_random)
X_test = masker.transform(X_figure)
#We load the visual stimuli from csv files
y_train = []
for y in y_random:
y_train.append(np.reshape(np.loadtxt(y, dtype=np.int, delimiter=','), (-1,) + y_shape, order='F'))
y_test = []
for y in y_figure:
y_test.append(np.reshape(np.loadtxt(y, dtype=np.int, delimiter=','), (-1,) + y_shape, order='F'))
X_train = np.vstack([x[2:] for x in X_train])
y_train = np.vstack([y[:-2] for y in y_train]).astype(float)
X_test = np.vstack([x[2:] for x in X_test])
y_test = np.vstack([y[:-2] for y in y_test]).astype(float)
n_pixels = y_train.shape[1]
n_features = X_train.shape[1]
def flatten(list_of_2d_array):
flattened = []
for array in list_of_2d_array:
flattened.append(array.ravel())
return flattened
#Build the design matrix for multiscale computation
#Matrix is squared, y_rows == y_cols
y_cols = y_shape[1]
#Original data
design_matrix = np.eye(100)
#Example of matrix used for multiscale (sum pixels vertically)
#
# 0.5 *
#
# 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
# 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
# 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
# 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
# 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
# 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
height_tf = (np.eye(y_cols) + np.eye(y_cols, k=1))[:y_cols - 1] * .5
width_tf = height_tf.T
yt_tall = [np.dot(height_tf, m) for m in y_train]
yt_large = [np.dot(m, width_tf) for m in y_train]
yt_big = [np.dot(height_tf, np.dot(m, width_tf)) for m in y_train]
#Add it to the training set
y_train = [np.r_[y.ravel(), t.ravel(), l.ravel(), b.ravel()] for y, t, l, b in zip(y_train, yt_tall, yt_large, yt_big)]
y_test = np.asarray(flatten(y_test))
y_train = np.asarray(y_train)
#Remove rest period
X_train = X_train[y_train[:, 0] != -1]
y_train = y_train[y_train[:, 0] != -1]
X_test = X_test[y_test[:, 0] != -1]
y_test = y_test[y_test[:, 0] != -1]
#We define our Prediction function
#Create as many OMP(OrthogonalMatchingPursuit) as voxels to predict
clfs = []
n_clfs = y_train.shape[1]
for i in range(y_train.shape[1]):
clf = Pipeline([('selection', SelectKBest(f_classif, 500)), ('clf', OMP(n_nonzero_coefs=10))])
clf.fit(X_train, y_train[:, i])
clfs.append(clf)
#Run the prediction function
y_pred = []
for clf in clfs:
y_pred.append(clf.predict(X_test))
y_pred = np.asarray(y_pred).T
# We need to the multi scale reconstruction
def split_multi_scale(y, y_shape):
#Split data into 4 original multi_scale images
yw, yh = y_shape
#Index of original image
split_index = [yw * yh]
#Index of large image
split_index.append(split_index[-1] + (yw - 1) * yh)
#Index of tall image
split_index.append(split_index[-1] + yw * (yh - 1))
#Index of big image
split_index.append(split_index[-1] + (yw - 1) * (yh - 1))
#We split according to computed indices
y_preds = np.split(y, split_index, axis=1)
#y_pred is the original image
y_pred = y_preds[0]
#y_pred_tall is the image with 1x2 patch application. We have to make
#some calculus to get it back in original shape
height_tf_i = (np.eye(y_cols) + np.eye(y_cols, k=-1))[:, :y_cols - 1] * .5
height_tf_i.flat[0] = 1
height_tf_i.flat[-1] = 1
y_pred_tall = [np.dot(height_tf_i, np.reshape(m, (yw - 1, yh))).flatten()
for m in y_preds[1]]
y_pred_tall = np.asarray(y_pred_tall)
#y_pred_large is the image with 2x1 patch application. We have to make
#some calculus to get it back in original shape
width_tf_i = (np.eye(y_cols) + np.eye(y_cols, k=1))[:y_cols - 1] * .5
width_tf_i.flat[0] = 1
width_tf_i.flat[-1] = 1
y_pred_large = [np.dot(np.reshape(m, (yw, yh - 1)), width_tf_i).flatten()
for m in y_preds[2]]
y_pred_large = np.asarray(y_pred_large)
#y_pred_big is the image with 2x2 patch application. We use previous
#matrices to get it back in original shape
y_pred_big = [np.dot(np.reshape(m, (yw - 1, yh - 1)), width_tf_i)
for m in y_preds[3]]
y_pred_big = [np.dot(height_tf_i, np.reshape(m, (yw - 1, yh))).flatten()
for m in y_pred_big]
y_pred_big = np.asarray(y_pred_big)
return (y_pred, y_pred_tall, y_pred_large, y_pred_big)
y_pred, y_pred_tall, y_pred_large, y_pred_big = split_multi_scale(y_pred, y_shape)
y_pred = (.25 * y_pred + .25 * y_pred_tall + .25 * y_pred_large + .25 * y_pred_big)
#Check the Scores of the model
print("Scores")
print("------")
print(" - Accuracy (percent): %f" % np.mean([
accuracy_score(y_test[:, i], y_pred[:, i] > .5) for i in range(100)]))
print(" - Precision: %f" % np.mean([
precision_score(y_test[:, i], y_pred[:, i] > .5) for i in range(100)]))
print(" - Recall: %f" % np.mean([
recall_score(y_test[:, i], y_pred[:, i] > .5) for i in range(100)]))
print(" - F1-score: %f" % np.mean([
f1_score(y_test[:, i], y_pred[:, i] > .5) for i in range(100)]))
#Finally we plot the Images
for i in range(6):
j = 10 * i
fig = plt.figure()
sp1 = plt.subplot(131)
sp1.axis('off')
plt.title('Stimulus')
sp2 = plt.subplot(132)
sp2.axis('off')
plt.title('Reconstruction')
sp3 = plt.subplot(133)
sp3.axis('off')
plt.title('Binarized')
sp1.imshow(np.reshape(y_test[j], (10, 10)), cmap=plt.cm.gray,
interpolation='nearest'),
sp2.imshow(np.reshape(y_pred[j], (10, 10)), cmap=plt.cm.gray,
interpolation='nearest'),
sp3.imshow(np.reshape(y_pred[j] > .5, (10, 10)), cmap=plt.cm.gray,
interpolation='nearest')
show()